Introduction
Parser
A parser is a YAML configuration file that describes how a string must be parsed. Said string can be a log line, or a field extracted from a previous parser.
While a lot of parsers rely on the GROK approach (a.k.a regular expression named capture groups), parsers can also use expressions to perform parsing on specific data (ie. json), refer to external methods for enrichment or even perform whitelisting.
The event enters the parser, and might exit successfully or not:
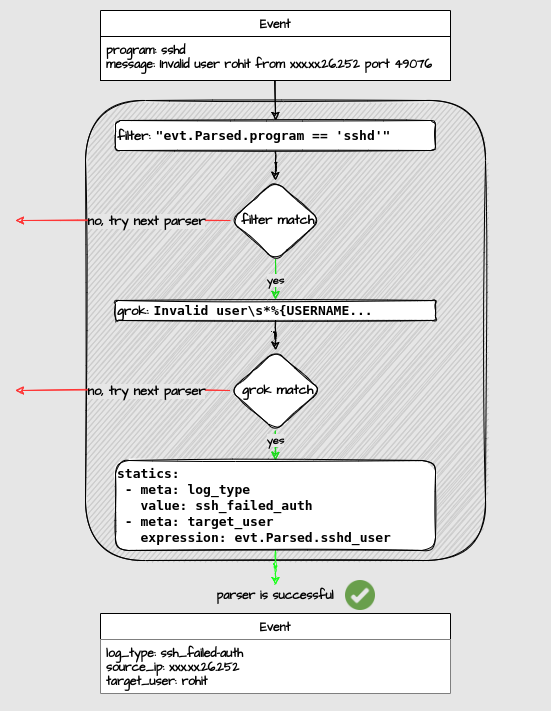
Stages
Parsers are organized into stages to allow pipelines and branching in parsing. An event can go to the next stage if at least one parser in the given stage parsed it successfully while having onsuccess set to next_stage. Otherwise, the event is considered unparsed and will exit the pipeline (and be discarded):
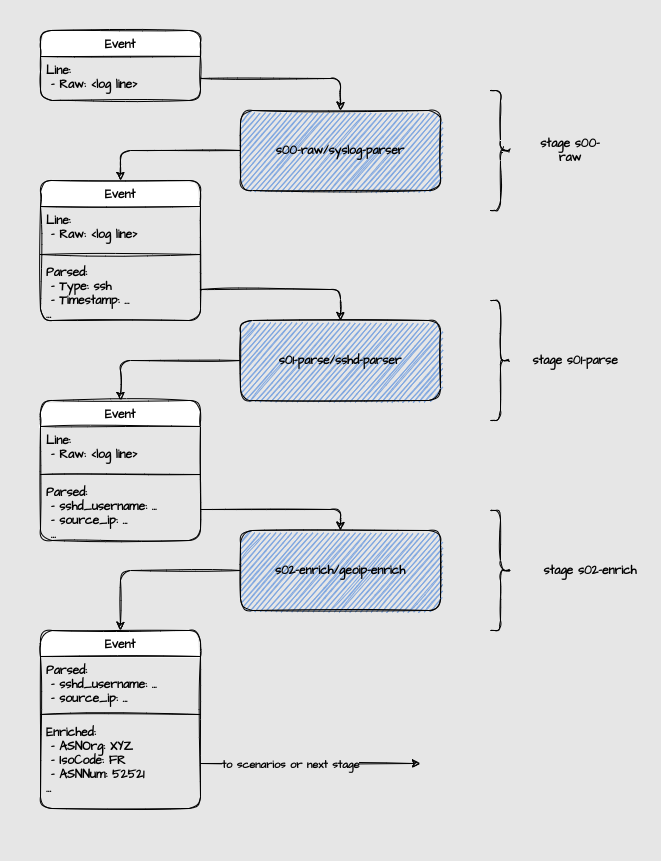
The parsing pipeline is broken down into multiple stages:
s00-raw: This is the first stage which aims to normalize the logs from various Data Sources into a predictable format fors01-parseands02-enrichto work on.s01-parse: This is the second stage responsible for extracting relevant information from the normalized logs based on the application type to be used bys02-enrichand the Scenarios.s02-enrich: This is the third stage responsible for enriching the extracted information with additional context such as GEOIP, ASN etc.
s00-raw
This stage is responsible for normalizing logs from various Data Sources into a predictable format for s01-parse and s02-enrich to work on.
For example if you have a syslog Data Source and a container Data Source writing the same application log lines you wouldnt want s01-parse to handle this logic twice, since s00-raw can normalize the logs into a predictable format.
For most instances we have already created these s00-raw parsers for you are available to view on the Hub.
s01-parse
The stage is responsible for extracting relevant information from the normalized logs based on the application type.
The application type is defined in different ways based on the Data Source. Please refer to the Data Sources documentation for more information.
We list all available applications we support on the Hub and within the readme of the collection our users provide an example Acquisition configuration.
s02-enrich
The aim of this stage is to enrich the extracted information with additional context such as GEOIP, ASN etc.
However, the stage can also be used to perform whitelist checks, however, we have dedicated documentation for this here.
Currently we have a few enrichers available on the Hub, that are installed by default so you dont need to worry about this stage unless you want to create your own.
Postoverflows
Once a scenario overflows, the resulting event is going to be processed by a distinct set of parsers, called "postoverflows".
Those parsers are located in /etc/crowdsec/postoverflows/ and typically contain additional whitelists, a common example is to whitelist decisions coming from some specific FQDN.
Usually, those parsers should be kept for "expensive" parsers that might rely on external services.
See the Hub to explore parsers, or see below some examples:
The parsers usually reside in /etc/crowdsec/parsers/<STAGE>/.

